Customer Journey: Understanding and Optimizing the Path to Customer Satisfaction
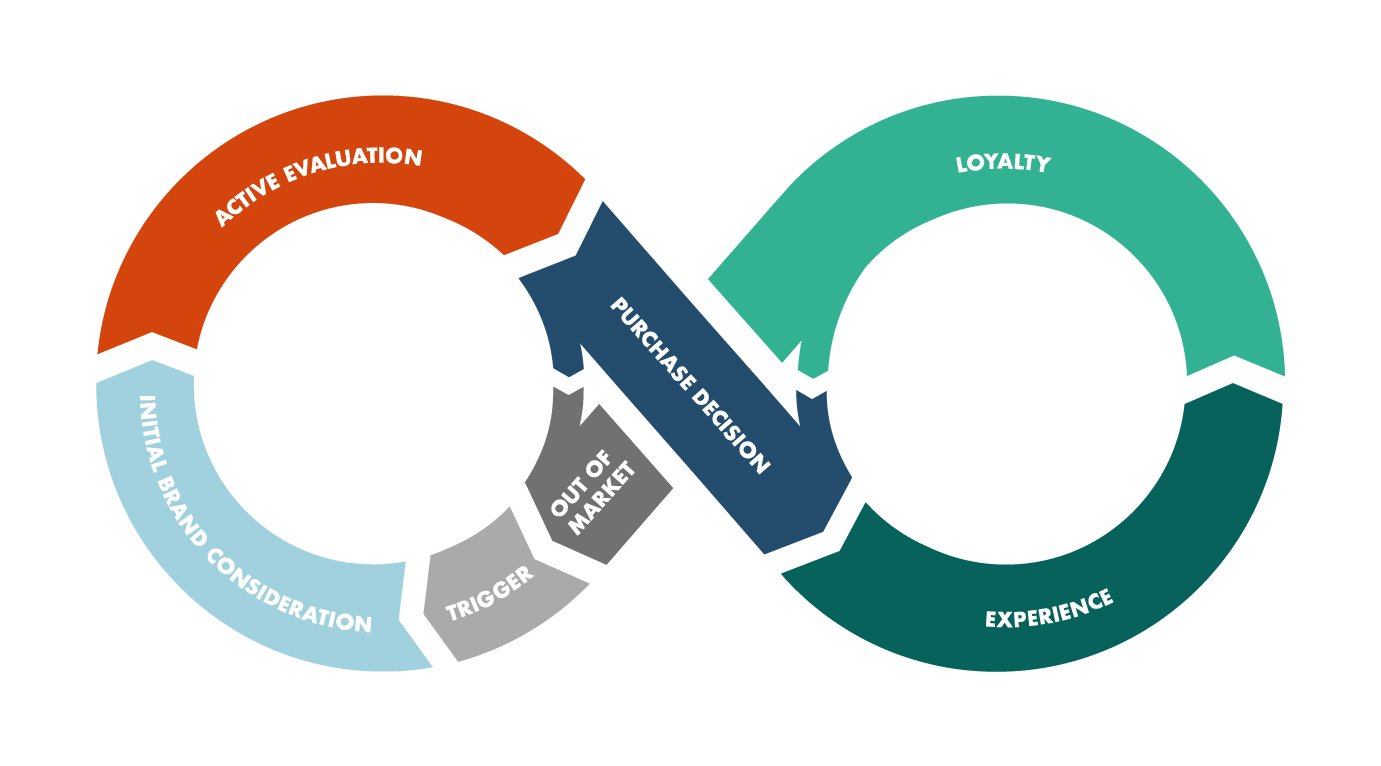
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the Customer Journey?
The customer journey refers to the series of interactions a customer has with a brand over time, beginning from the moment they first become aware of a product or service, through the consideration and decision-making process, and continuing after a purchase has been made. This journey can take place across multiple channels and touchpoints, including in-person interactions, websites, social media, mobile apps, and customer support.
The customer journey is not linear and can vary for different individuals. A person might go through a series of touchpoints at different speeds or skip certain stages entirely, depending on their needs, preferences, and behavior. Understanding this journey is crucial for businesses to tailor their marketing, sales, and customer service efforts to meet customers where they are.
Stages of the Customer Journey
The https://roman-business .com typically consists of several stages, which can vary slightly depending on the business model and customer behavior. However, the journey can generally be broken down into the following key stages:
1. Awareness
- Definition: The awareness stage is when a potential customer first becomes aware of a problem or need and starts looking for solutions. This is the first interaction a customer has with a brand, often triggered by marketing campaigns, word-of-mouth referrals, social media, or organic search results.
- Objective for Businesses: At this stage, your goal is to capture the attention of the customer. This can be done through educational content, engaging advertisements, blog posts, social media content, and SEO efforts that make your brand visible to those looking for a solution to their problem.
- Example: A person searching for “how to improve sleep quality” may come across a blog post or video from a sleep product company that educates them on the importance of quality mattresses.
2. Consideration
- Definition: In the consideration stage, the customer has already identified their problem and is now considering various solutions. This stage involves deeper research and evaluation of different options available to them.
- Objective for Businesses: Here, your goal is to provide more detailed information that helps customers compare your offerings with competitors. This could include case studies, product demonstrations, comparison charts, reviews, or testimonials that showcase how your product or service solves their problem better than alternatives.
- Example: After reading the initial blog, the potential customer might download a free guide or request a product demo to learn more about your mattress and how it can improve their sleep quality.
3. Decision
- Definition: The decision stage is when the customer has narrowed down their options and is ready to make a purchase. They will weigh the pros and cons of each solution and choose the one that best meets their needs and expectations.
- Objective for Businesses: At this point, businesses should focus on providing any final push that makes the purchase decision easy and compelling. This could involve offering discounts, free trials, customer support, or limited-time promotions. The key here is to build trust and offer clear calls to action that make it easy for the customer to buy.
- Example: The customer might visit the product page of your website, see customer reviews, and then make a purchase with the help of a “special offer” or “free shipping” incentive.
4. Retention
- Definition: Retention focuses on keeping customers happy and engaged after the initial purchase. At this stage, the goal is to foster loyalty, encourage repeat purchases, and create long-term relationships.
- Objective for Businesses: The retention stage involves maintaining a strong relationship with customers through excellent customer service, personalized communication, loyalty programs, follow-up emails, and consistent value delivery. Businesses should continue to engage customers and provide ongoing support or product education to keep them satisfied.
- Example: After purchasing the mattress, the customer receives personalized emails with sleep tips, product care instructions, and offers for other related products, such as pillows or mattress protectors.
5. Advocacy
- Definition: The advocacy stage occurs when satisfied customers share their positive experiences with others, either through word-of-mouth, social media posts, or online reviews. These customers may become brand ambassadors, referring others to the product or service.
- Objective for Businesses: Encourage customers to advocate for your brand by providing incentives like referral programs, social sharing opportunities, and asking for reviews or testimonials. Happy customers who share their experiences can help drive new customer acquisition.
- Example: A satisfied customer leaves a glowing review on your website or social media, or they refer a friend to your brand, helping to create a new customer.
Mapping the Customer Journey
Mapping the customer journey involves visually representing the different stages a customer goes through, along with the touchpoints and interactions they have with the brand at each stage. By mapping the journey, businesses can identify pain points, gaps in the experience, and opportunities for improvement.
Steps to Map the Customer Journey:
-
Identify Customer Personas: Understanding who your customers are, their needs, behaviors, and pain points is the first step in mapping the customer journey. Create detailed customer personas to represent different segments of your audience.
-
List Key Touchpoints: Touchpoints are the interactions a customer has with your brand. These can include browsing your website, engaging with social media posts, receiving emails, interacting with customer service, or visiting your store.
-
Analyze Customer Emotions: Understanding how customers feel at each stage of the journey is essential. Are they excited, frustrated, confused, or satisfied? Identifying emotions can help you design a better experience that addresses pain points.
-
Identify Opportunities for Improvement: Once you’ve mapped the journey, look for areas where the customer experience could be enhanced. Are there stages where customers drop off? Are there touchpoints that need better engagement?
-
Optimize the Journey: Use insights gained from mapping to create a more cohesive, personalized, and streamlined experience. This might involve improving your website’s navigation, offering better support at the decision stage, or engaging more with customers during the post-purchase phase.
How to Optimize the Customer Journey
To ensure that the customer journey is as smooth and effective as possible, businesses should focus on several strategies:
1. Personalization
- Personalization is crucial in delivering a relevant experience. Use data from customer interactions to tailor content, recommendations, and offers based on individual behaviors, preferences, and previous purchases.
- Example: If a customer has purchased a product before, offer them personalized recommendations for complementary products or services.
2. Omnichannel Experience
- Customers interact with brands across various channels (web, social media, in-store, email, etc.). Ensuring a consistent experience across all channels is critical. Customers should be able to move seamlessly from one touchpoint to another without feeling disconnected.
- Example: If a customer browses a product online and then visits a store, the store associates should be aware of their online interests and offer personalized assistance.
3. Clear Communication
- Clear, transparent, and timely communication at every stage of the customer journey can help build trust. Provide easy access to support and ensure customers know what to expect at each step, from shipping times to return policies.
- Example: Send order confirmation emails, shipping notifications, and follow-up messages after purchase to keep customers informed.
4. Streamlined Processes
- Customers value convenience, so it’s essential to streamline processes like purchasing, signing up, and accessing customer support. Minimizing steps or unnecessary complexity can improve satisfaction.
- Example: Offer a one-click purchase option or an easy-to-navigate checkout process that reduces cart abandonment.
5. Gather and Act on Feedback
- Continuously collect feedback from customers through surveys, reviews, or social media comments. Use this data to improve the customer journey at each touchpoint.
- Example: Send a post-purchase survey to gather feedback about the customer’s experience and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
The customer journey is not just about the sales funnel—it’s about building lasting relationships with customers by offering them a seamless, personalized, and engaging experience at every touchpoint. By understanding the stages of the journey and optimizing each one, businesses can drive customer satisfaction, increase conversions, and foster loyalty.
Mapping and improving the customer journey is an ongoing process that requires businesses to stay in tune with customer needs and continuously adapt to changes. With a strong focus on personalization, omnichannel consistency, and customer feedback, brands can create experiences that not only meet but exceed customer expectations, leading to long-term success.
.jpg)